
Instead, the consignee only records the sale and the corresponding cost of goods sold when the items are actually sold. This arrangement helps mitigate the risk for the consignee while providing the consignor with a broader distribution network. The consignee also has the option to return the consignment inventory if it fails to sell it. The treatment for the return is similar to that of the initial transfer. For the consignor, the return does not specify any changes in risks and rewards.
Consignment Inventory Journal Entry
However, if the consignor had transferred the goods to a temporary consignment inventory account, it must reverse the accounting treatment. If you’re selling on consignment as well as through other channels like an online shop, it’s important to make sure you keep your consignment inventory accounting records separate. The reason for this is that the cost of goods sold (COGS) for your consignment inventory will likely be different than your COGS for inventory sold through other channels. Accounting for consignment inventory requires careful consideration of revenue recognition, inventory valuation, and commission expenses.
Inventory Tracking
They can track sales more quickly and replenish consignments from the supplier’s warehouse as needed. It would be challenging for retailers to track their margins, making it tough to profit because these consigned items do not include any upfront supply costs. When practicing consignment accounting, the process begins when the consignee receives goods. The journal entry for the consignment accounting will have a credit and a debit. It is recorded as a debit for the consignment inventory, and a credit for the store’s inventory. Consignment inventory is a supply chain management strategy where a supplier (consignor) places its products in the possession of a retailer (consignee), who then sells the goods to customers.
Consignee sells the inventory journal entry
The consignor must wait until the consignee sells the goods to a third party before recognizing revenue. This delay ensures that the revenue is both earned and realizable, adhering to standard accounting principles. Securing the right technology for effective consignment inventory management is pivotal for the success of such partnerships. Your organization will benefit from a specialized solution, a consignment management system like PALMS™ Smart WMS. It is a warehouse digital transformation tool that offers a unified, real-time inventory view across all locations and sales channels. This supply chain model is often adopted by retailers with limited financial resources, particularly for expensive, slow-moving products.
For example, you should stipulate what commission, if any, the consignee will charge the consignor and the intervals a consignee will make payments for sold inventory. Inventory items that are sold through the consignment model are often perishable, seasonal, or previously owned. The consignee now provides a summary to the consignor of all transactions it has made relating to the consignment. This agreement will serve as a contract between the consignor and consignee, binding each party to perform their roles and responsibilities in the transaction. The consignee also keeps a percentage of the sale proceeds and pays the consignor a predetermined sales amount. No one should act upon such information without appropriate professional advice after a thorough examination of the particular situation.
- In exchange, businesses can avoid any potential markdowns or inventory losses and not have to bear the expense of consignment goods that do not sell.
- Here’s a quick list of pros and cons to help you decide whether to give consignment a shot or stick to more traditional methods.
- Only once the consignment inventory is sold would a transaction for a sale be created for accounting purposes.
- Since the risks and rewards of the goods do not transfer due to the transfer, the consignor cannot record the inventory as sold.
- He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries.
IAS 2 accounting for storage, shipping and handling costs may differ from US GAAP
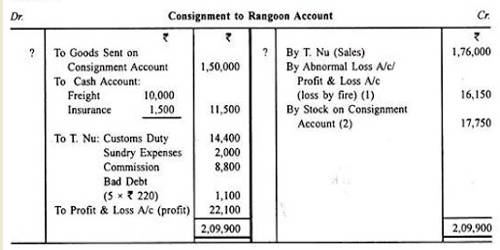
Consignment inventory refers to an inventory arrangement that results from an agreement. This agreement mostly specifies that one party must hold inventory for another party for a specific purpose. The NET effect of these transactions and journal entries would be summarised the history of tax day in the income statement reflected as below. The consignee pays the import duty of $200 and selling expenses of $300. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting.
By embracing this innovative approach, businesses can unlock new growth opportunities and establish mutually beneficial partnerships with suppliers and retailers. The consignment expenses incurred are the cost of bringing the inventory to its present location and are debited to the consignment inventory account. Depending on the terms agreed with the consignor the journal entry is either to accounts payable or cash credit and no entry is made by the consignee. In case the consignee returns unsold goods, the consignor doesn’t need any accounting entries.
We promise that using this software will significantly simplify the management of your consignment inventory project. A retailer takes on a significant financial risk when they agree to purchase most of a product’s stock. Since they have a common goal, they build relationships with their suppliers the more they market and advertise the consignment products. There’s always a chance they won’t like the new thing and leave retailers stuck with unsold inventory.
